Why should I use the Knowledge Library?
IFMA’s Knowledge Library contains information on the latest trends and expert advice in the industry. Learn best practices and advance your facility management career.
Achieve your career goals faster
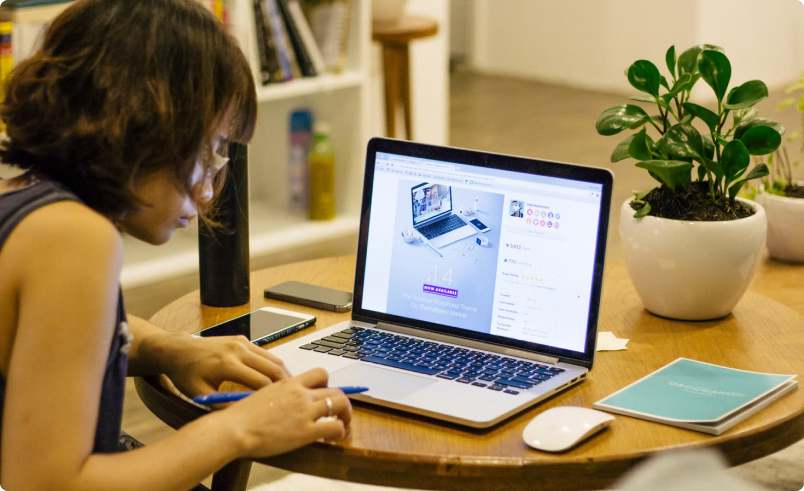

Get answers and share resources

Learn Key Concepts

Become part of the largest global FM community
Join IFMA so you can access industry-leading resources from experts in facility management.
Step 1. Join IFMA
Join IFMA so you can access to the best thought leadership and industry-leading resources in facility management.
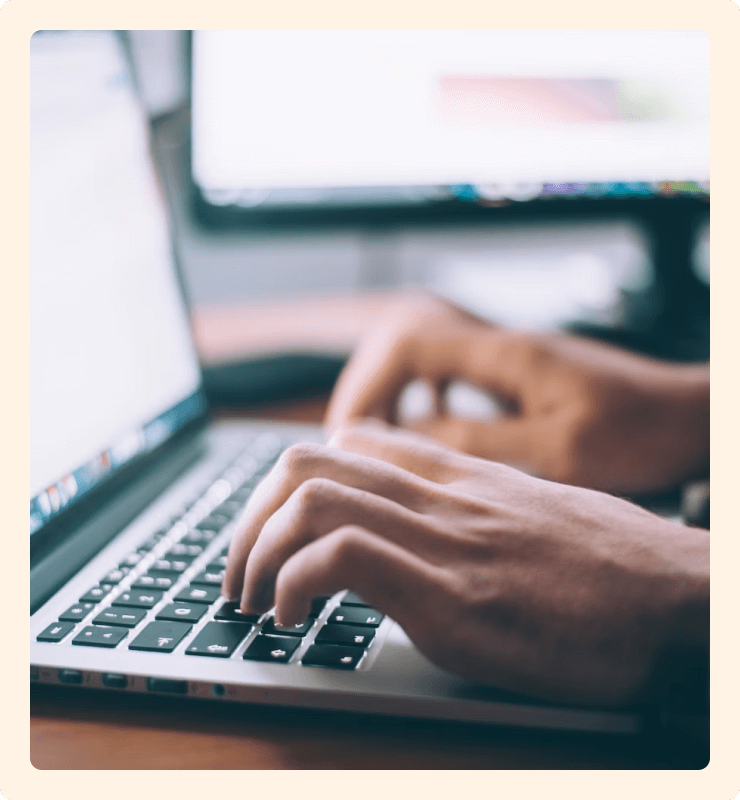

Step 2. Sign In To Knowledge Library
Full IFMA members can access the entire Knowledge Library.

Step 3. Access Content And Learn
Learn from informative content written by experts in the facility management industry – and apply it to you career.

Still Have Questions?
What can I expect from the Knowledge Library?
Get the latest content and resources and learn the newest trends in facility management. The Knowledge Library is a reference tool that will help you expand your knowledge so you can grow professionally.
Can I use the Knowledge Library for free?
Full IFMA members gain access for free with their annual membership. A limited number of articles are available with a nonmember account. Find out more.
What is included in the Knowledge Library?
The Knowledge Library contains articles, case studies, research, benchmarking reports, videos, webinars, templates and more.
How is the Knowledge Library different from other FM content sites?
Knowledge Library content is created by FM industry thought leaders from around the world. Each piece of content is reviewed for value, quality and relevance to the FM industry.
Is there a free trial?
Sign up for a free account to view three (3) pieces of content a month.
Can I submit something for consideration to be published?
Yes! All FM thought leaders are welcome to submit content to support facility professionals and add to the collective body of knowledge. Learn more.


What Our Members Are Saying
Learn about the value IFMA’s information brings to our members.
Jagun Associates
relevant articles, videos, posts and toolkits that support our membership globally.”